Unternehmen
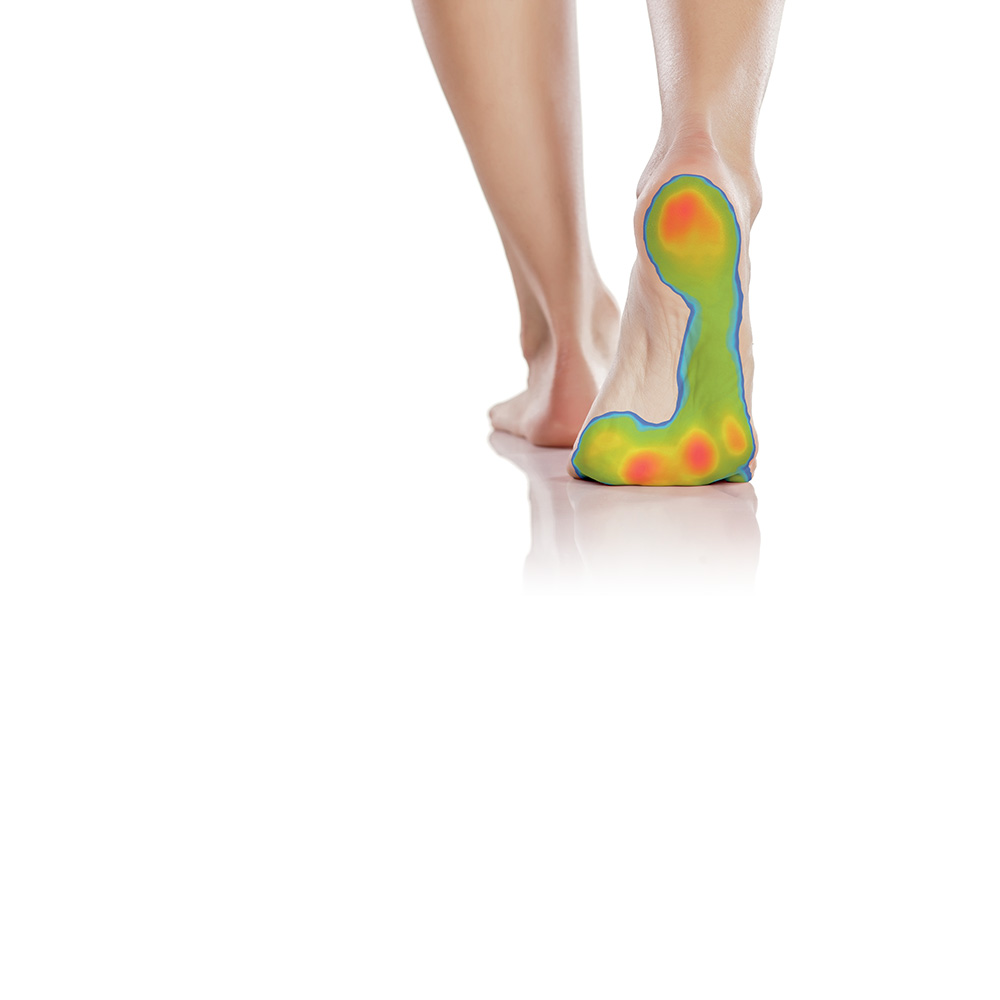
Hier finden Sie typische Einsatzgebiete der Pedobarometrie (Polizei, Feuerwehr, Armee):
- Unterstützung Zentraleinkauf/Beschaffung
- Kontrolle der korrekten Sportschuhversorgung (Arbeitsschutz)
- Schuhempfehlung
- Analyse Abrollverhalten
- Baseline-Ermittlung (Monitoring)
- Einlagenversorgung (Betriebsarzt)
Forschung
Hier finden Sie typische Einsatzgebiete der Pedobarometrie:
- Ermittlung von Druckverteilungen
- Ermittlung Bodenkontaktzeiten
- Ermittlung Timing-Parameter
- Leisten- und Sportschuhbau
- Bewegungsanalyse
Veterinärmedizin
Hier finden Sie typische Einsatzgebiete der Pedobarometrie:
- Ermittlung der Belastungsverteilung (Kuh)
- Kontrolle Hufbeschlag (Pferd)
- Veterinärmedizin (Kleintier)
- Forschungsfragen (Veterinärmedizin)
Einsatzgebiete
Mit der Eweiterung des RSscan Portfolios um leistungsstarke 3D-Scanner, bieten wir unseren Kunden die perfekte Ergänzung zur Analyse und weitergehenden Nutzung wertvoller Daten rund um das Thema Leisten- und Schuhbau.
Darüber hinaus lassen sich die erhobenene Daten sehr gut zur prä- und postoperativen Diagnostik im medizinischen Bereich nutzen, beispielsweise zur Diagnose und Kontrolle von Achillessehnenverletzungen.
Scanner-Modelle
Tiger 3D Scanner
Erstellen Sie einen kompletten und detaillierten 3D Scan Ihres Fußes. Die Scanhöhe über Sprunggelenk erlaubt eine vielseitige Verwendung der Analysedaten.
Die footscan essentials Software erlaubt die integrierte Messung, die Berechnung der Längsgewölbehöhe (arch height), die räumliche Betrachtung der Messung am Bildschirm Export von STL Daten für die weiterführende Verarbeitung in aneren 3D Design Programmen oder für die verarbeitung in CAM Maschinen.
- Kameras: 9 Kameras (8 x color, 1 x monochrom)
- Meßgenauigkeit +/- 0.5 mm
- Messdauer: 5-15 Sekunden
- Gewicht: 26 kg
- Größe:76 cm x 83 cm x 122 cm
Preisanfragen stellen Sie bitte direkt an info@evoletics.de.
iQube Scanner (E500)
Dieser Scanner eignet sich für die Erfassung der plantarseite des Fußes sowie zum Digitalisieren von Trittschaumabdrücken. Der iQube erzeugt hochqualitative 3D Daten in Sekundenschnelle. Sparen Sie Zeit und Energie bei Routineaufgaben (Vermessung von Fußlänge, Fußbreite, Gewölbehöhe) und konzentrieren Sie sich wieder auf die Kundenbetreuung und den Bau qualitativer Einlagen.
- Kameras: 5 Kameras
- Meßgenauigkeit +/- 0.4mm
- Messdauer: 5-9 Sekunden
- Gewicht: 17 kg
- Größe: 70 cm x 38 cm x 20 cm
iQube Mini Scanner (E100)
Noch kleiner, noch handlicher, noch schneller. Der iQube Mini ist der Einstiegsscanner zum Erfassen von 3D Fußabdrücken (plantar), von Kundeneinlagen oder anderen Gegenständen. Er erzeugt präzise 3D Bilder und ist hervorragend für den mobilen Einsatz geeignet..
- Kameras: 1 Kamera
- Meßgenauigkeit: +/- 1mm
- Meßgeschwindigkeit: 5-7 Sekunden
- Gewicht: 6 kg
- Abmessungen: 54 cm x 29 cm x 8 cm
Messdaten
Sie haben Interesse an Messdaten, dann haben Sie hier die Möglichkeit ein Set an Messdaten herunterzuladen.
STL Testdaten
STL Testdaten der drei Scannermodelle finden Sie unter folgender URL als ZIP Datei zum Download: Scanner, Meßdaten 1, Meßdaten 2. Diese können für Testzwecke in Ihrer bestehenden Anwendungsum-gebung verwendet werden.
Software Development Kit:
Mit Hilfe des SDK (Software Development Kit) können Sie eigene Anwendungssoftware für Ihre Kunden schreiben und die gelieferte Hardware nach Ihren Wünschen entsprechend steuern. Je nach Anzahl der vertriebenen Geräte pro Kalenderjahr ist das SDK bei Kleinstmengen kostenfrei, bei größeren Umsatzmengen kostenpflichtig. Weitere Details können wir gern mit Ihnen besprechen.
Einsatzgebiete
Die Einsatzmöglichkeiten der Pedobarometrie sind sehr vielfältig
3D Scanner
3D Scanner finden eine immer weitere Verbreitung und sind inzwischen auch in der Orthopädietechnik angekommen. Überzeugen Sie sich von den vielfältigen Einsatzmöglichkeiten dieser Technik oder schauen Sie sich die Technik bei einem Demonstrationstermin genauer an. Wir unterstützen Sie gern, die richtige Technik für Ihre Anforderungen zu finden.

Bewegungsanalyse
Die evoletics Bewegungsanalyse ermöglicht Ihnen den Zugriff auf das komplette Sortiment von RSscan International (Belgien) zu den Themen dynamische Pedobarometrie, 3D Scanning sowie der Herstellung individueller 3D gedruckter Einlagen. Zusätzlich bieten wir zusammen mit unseren Netzwerkpartnern weitere diagnostische Verfahren und Dienstleistungen rund um das Thema Bewegungsanalyse an.

Wenn Sie mit Maßschuhen, der Herstellung von individuellen Leistenformen oder der Einlagenversorgung zu tun haben, dann werden Sie zukünftg nicht an leistungsstarken 3D Scanner vorbeikommen. Bei uns sind sie bereits in unserer footscan Software integriert, können aber auch autonom betrieben werden. Selbstverständlich können Sie auch unser spezielles SDK (Software Developer Kit) nutzen, um die Scanner Hardware in Ihre Softwareumgebung zu integrieren. 
footscan Systeme von RSscan bieten neben der dynamischen Fußdruckmessung auch die Möglichkeit der Einlagenversorgung durch 3D gedruckte Einlagen. Unter dem Markenname Phits gelangen Sie so in einem Arbeitsschritt von der Anamnese über die Diagnostik bis hin zur Versorgung. Überzeugen Sie sich von einer völlig neuen Qualitätsstufe.

Profitieren Sie zusätzlich von unseren langjährigen Erfahrungen aus der Sportwissenschaft, dem Leistungssport oder unsererem universitären Netzwerk. Im Vordergrund der Beratung und Versorgung stehen hier vor allem Fragen der Belastungsverträglichkeit, biomechanische Aspekte der Schuhversorgung und Fragen der korrekten Schuhauswahl in verschiedensten Sportarten. Einen besonderen Service bieten wir auch Schuhherstellern im Rahmen des Sportsponsorings von Vereinen und Einzelsportlern.

Bei Fragen nutzen Sie bitte unser Kontaktformular.
Literatur und Forschung
- Abboud RJ, Rowley DI, Lower limb muscle dysfunction may contribute to foot ulceration in diabetic patients (…)
- Alexander RM, Jayes AS, Fourier analysis of forces exerted in walking and running (…)
- Andrews S, The effectiveness of footwear orthoses and casted devices in redistributing plantar pressure a systematic review of literature (…)
- Arndt A., Correction for sensor creep in the evaluation of long-term plantar pressure data. (…)
- Bauml C, Die sprunggelenksnahe Unterschenkelfraktur im Kindes- und Jugendlichenalter: Klinische und biomechanische Nachuntersuchung nach operativer Versorgung (…)
- Beaulieu FG, Pelland L, Robertson DG, Kinetic analysis of forwards and backwards stair descent. (…)
- Beil TL, Street GM, Covey SJ., Interface pressures during ambulation using suction and vacuum-assisted prosthetic sockets. (…)
- Bisiaux, Moretto, The effects of fatigue on plantar pressure distribution in walking (…)
- Biswas, Lemaire and Kofman, Dynamic gait stability index based on plantar pressures and fuzzy logic (…)
- Bosch K, Gerss J, Rosenbaum D., Preliminary normative values for foot loading parameters of the developing child. (…)
- Bourrel, Study of pressure distribution in different leprosy footwear (…)
- Bransby-Zachary M A, Stother I G and Wilkinson R, Peak pressures in the forefoot (…)
- Brodtkorb TH, Kogler GF, Arndt A., The influence of metatarsal support height and longitudinal axis position on plantar foot loading. (…)
- Bryant, Tinley, Cole, Plantar Pressure and Joint Motion After the Youngswick Procedure for Hallux Limitus (…)
- Burnfield JM, Few CD, Mohamed OS, Perry J., The influence of walking speed and footwear on plantar pressures in older adults. (…)
- Burnfield JM, Jorde AG, Augustin TR, Augustin TA, Bashford GR., Variations in plantar pressure variables across five cardiovascular exercises (…)
- Burns J, Crosbie J, Hunt A, The Effect of Pes Cavus on Foot Pain and Plantar Pressure (…)
- Bus SA, Foot structure and footwear prescription in diabetes mellitus. (…)
- Bus SA, de Lange A., A comparison of the 1-step, 2-step, and 3-step protocols for obtaining barefoot plantar pressure data in the diabetic neuropathic foot. (…)
- Bus SA, Maas M, de Lange A, Michels RP, Levi M., Elevated plantar pressures in neuropathic diabetic patients with claw/hammer toe deformity. (…)
- Bus SA, Ulbrecht JS, Cavanagh PR., Pressure relief and load redistribution by custom-made insoles in diabetic patients with neuropathy and foot deformity. (…)
- Bus SA, Valk GD, van Deursen RW, Armstrong DG, Caravaggi C, Hlavácek P, Bakker K, Cavanagh PR., The effectiveness of footwear and offloading interventions to prevent and heal foot ulcers and reduce plantar pressure in diabetes: a systematic review. (…)
- Carl , Putz, Weseloh, Forst und Swoboda, Die Einlagenversorgung des rheumatischen Fußes (…)
- Caselli A, Pham H, Giurini JM, Armstrong DG, Veves A., The forefoot-to-rearfoot plantar pressure ratio is increased in severe diabetic neuropathy and can predict foot ulceration. (…)
- Cavanagh P; Rodgers M, The arch index: a useful measure from footprints (…)
- Chang A, Hurwitz D, Dunlop D, Song J, Cahue S, Hayes K, Sharma L., The relationship between toe-out angle during gait and progression of medial tibiofemoral osteoarthritis. (…)
- Chedevergne F, Dahan M, Faivre A, A new mechatronical device for determining human plantar pressure (…)
- Chesnin KJ, Selby-Silverstein L, Besser MP., Comparison of an in-shoe pressure measurement device to a force plate: concurrent validity of center of pressure measurements. (…)
- Chuckpaiwong B, Mall N, Queen R, Nunley JA, The effect of foot type on in shoe plantar pressure during walking and running (…)
- Chuckpaiwong B, Nunley JA, Mall NA, Queen RM., The effect of foot type on in-shoe plantar pressure during walking and running. (…)
- Commean PK, Mueller MJ, Smith KE, Hastings M, Klaesner J, Pilgram T, Robertson DD., Reliability and validity of combined imaging and pressures assessment methods for diabetic feet. (…)
- Cong, Luximon and Zhang, Effect of Shank Curve of High-heeled Shoe on the Plantar Pressure Distribution (…)
- Crenshaw SJ, Pollo FE, Brodsky JW., The effect of ankle position on plantar pressure in a short leg walking boot. (…)
- CROWTHER Robert G. ; SPINKS Warwick L. ; LEICHT Anthony S. ; QUIGLEY Frank; GOLLEDGE Jonathan;, Relationship between temporal-spatial gait parameters, gait kinematics, walking performance, exercise capacity, and physical activity level in peripheral arterial disease (…)
- Dai XQ, Li Y, Zhang M, Cheung JT., Effect of sock on biomechanical responses of foot during walking (…)
- De Cock A, Vanrenterghem J, Willems T, Witvrouw E, De Clercq D., The trajectory of the centre of pressure during barefoot running as a potential measure for foot function. (…)
- De Cock A., The use and interpretation of plantar pressure measurements during running (…)
- De Cock A, Willems T, Witvrouw E, Vanrenterghem J, De Clercq D., A functional foot type classification with cluster analysis based on plantar pressure distribution during jogging. (…)
- De Cock A; De Clercq D; Willems T; Witvrouw E, Temporal characteristics of foot roll-over during barefoot jogging: reference data for young adults (…)
- Descatoire A, Moretto P, Does B.I.R.D foot control supply sensitivity disturbance induced by emla cream anaesthesia (…)
- Dhukaram V, Hullin MG, Senthil Kumar C., The Mitchell and Scarf osteotomies for hallux valgus correction: a retrospective, comparative analysis using plantar pressures. (…)
- Dinh TL, Veves A., A review of the mechanisms implicated in the pathogenesis of the diabetic foot. (…)
- Dixon S; McNally K; Stiles V, Influence of orthotic devices prescribed using pressure data on lower extremity kinematics and pressures beneath the shoe during running (…)
- Dixon SJ, McNally K., Influence of orthotic devices prescribed using pressure data on lower extremity kinematics and pressures beneath the shoe during running (…)
- Dixon SJ., Application of center-of-pressure data to indicate rearfoot inversion-eversion in shod running. (…)
- Dixon SJ., Use of pressure insoles to compare in-shoe loading for modern running shoes. (…)
- Drerup B, Szczepaniak A, Wetz HH., Plantar pressure reduction in step-to gait: a biomechanical investigation and clinical feasibility study. (…)
- Erdemir A, Saucerman JJ, Lemmon D, Loppnow B, Turso B, Ulbrecht JS, Cavanagh PR., Local plantar pressure relief in therapeutic footwear: design guidelines from finite element models. (…)
- Erdemir A, Saucerman JJ, Lemmon D, Loppnow B, Turso B, Ulbrecht JS, Cavanagh PR., Local plantar pressure relief in therapeutic footwear: design guidelines from finite element models. (…)
- Fascione, JM.; Crews, RT.; Wrobel, JS, The Association of Foot Print Parameters and Running Training Level/Event Focus (…)
- FILIPPIN, NT; BARBOSA, VLP; SACCO, ICN and LOBO DA COSTA, PH., Effects of obesity on plantar pressure distribution in children (…)
- Finch P., Baskwill A., Marincola F., Becker P., Changes in pedal plantar pressure variability and contact time following massage therapy: A case study of a client with diabetic neuropathy (…)
- Firth J, Turner D, Smith W, Woodburn J, Helliwell P., The validity and reliability of PressureStat for measuring plantar foot pressures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. (…)
- Fong, Chan, Hong, Yung, Fung, Chan, Estimating the complete ground reaction forces with pressure insoles in walking (…)
- Ford KR, Manson NA, Evans BJ, Myer GD, Gwin RC, Heidt RS Jr, Hewett TE., Comparison of in-shoe foot loading patterns on natural grass and synthetic turf. (…)
- Fritsch R, Däumling S, Riehle H, ANALYSIS OF THE STABILIZING EFFECT OF THE AIRCAST ANKLE BRACE FOR WALKING ALONG AN INCLINED PLANE (…)
- Garrow, AP; van Schie, CH; Boulton, A.J., Efficacy of multilayered hosiery in reducing in-shoe plantar foot pressure in high-risk patients with diabetes (…)
- Giacomozzi C, Macellari V, Leardini A, Benedetti MG., Integrated pressure-force-kinematics measuring system for the characterisation of plantar foot loading during locomotion. (…)
- Giacomozzi C, Martelli F, Peak pressure curve: An effective parameter for early detection of foot functional impairments in diabetic patients (…)
- Giacomozzi C., Methodologies and measurement devices for an effective functional assesment of the diabetic foot (…)
- Girard O, Eicher F, Fourchet F, Micallef JP, Millet GP., Effects of the playing surface on plantar pressures and potential injuries in tennis. (…)
- Goske S, Erdemir A, Petre M, Budhabhatti S, Cavanagh PR., Reduction of plantar heel pressures: Insole design using finite element analysis. (…)
- Gravante, Pomara, Russo, Amato, Cappello, Ridola, Plantar pressure distribution analysis in normal weight young women and men with normal and claw feet: A cross-sectional study (…)
- Gröndal L., The rheumatoid forefoot – Surgical treatment and epidemiological aspects (…)
- Guldemond NA, Leffers P, Sanders AP, Schaper NC, Nieman F, Walenkamp GH., Daily-life activities and in-shoe forefoot plantar pressure in patients with diabetes. (…)
- Guldemond NA, Leffers P, Schaper NC, Sanders AP, Nieman F, Walenkamp G, Comparison of foot orthoses made by podiatrists, pedorthists and orthotists regarding plantar pressure reduction in The Netherlands (…)
- Gurney JK, Kersting UG, Rosenbaum D., Between-day reliability of repeated plantar pressure distribution measurements in a normal population. (…)
- Hagman F, van Gheluwe B., Influence of calcaneal eversion and navicular drop on the medial-lateral displacement of the center of pressure during gait (…)
- Hagman F., Can plantar pressure predict foot motion? (…)
- Hahn F, Maiwald C, Horstmann T, Vienne P., Changes in plantar pressure distribution after Achilles tendon augmentation with flexor hallucis longus transfer. (…)
- Hallemans A, de Clercq D, van Dongen S, Aerts P, Changes in foot-function parameters during the first 5 months after the onset of independent walking: a longitudinal follow-up study (…)
- Hennessy K, Burns J, Penkala S., Reducing plantar pressure in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison of running versus off-the-shelf orthopaedic footwear. (…)
- Hernandez A, Kimura LK, Laraya M, Fávaro E, Calculation of Staheli’s plantar arch index and prevalence of flat feet: a study with 100 children aged 5-9 years (…)
- Hessert MJ, Vyas M, Leach J, Hu K, Lipsitz LA, Novak V., Foot pressure distribution during walking in young and old adults. (…)
- Hillstrom H, Gait Analysis Tools from the Clinic to the Gait Lab: Applications for the Rheumatology Professional (…)
- HINZ P; HENNINGSEN A; MATTHES G; JAGER B; EKKEMKAMP A; ROSENBAUM D, Analysis of pressure distribution below the metatarsals with different insoles in combat boots of the German Army for prevention of march fractures (…)
- Hong Y, Wang L, Influence of shoe midsole material hardness on perceived comfort rearfoot motion and plantar pressure (…)
- Hosein R; Lord M, A study of in-shoe plantar shear in normals. (…)
- Hsu YC, Gung YW, Shih SL, Feng CK, Wei SH, Yu CH, Chen CS., Using an optimization approach to design an insole for lowering plantar fascia stress–a finite element study. (…)
- Hughes J., The clinical use of pedobarography. (…)
- Hurkmans HL, Bussmann JB, Benda E, Verhaar JA, Stam HJ., Accuracy and repeatability of the Pedar Mobile system in long-term vertical force measurements. (…)
- Hurkmans HL, Bussmann JB, Selles RW, Horemans HL, Benda E, Stam HJ, Verhaar JA., Validity of the Pedar Mobile system for vertical force measurement during a seven-hour period. (…)
- Isableu B, Vuillerme N., Differential integration of kinaesthetic signals to postural control. (…)
- Jaarsma, R.L., Ongkiehong, B.F., Grüneberg, C., Verdonschot, N., Duysens, J., van Kampen, A., Compensation for rotational malalignment after intramedullary nailing for femoral shaft fractures: An analysis by plantar pressure measurements during gait (…)
- Kang JH, Chen MD, Chen SC, Hsi WL. , Correlations between subjective treatment responses and plantar pressure parameters of metatarsal pad treatment in metatarsalgia patients: a prospective study. (…)
- Keijsers NL, Stolwijk NM, Nienhuis B, Duysens J., A new method to normalize plantar pressure measurements for foot size and foot progression angle. (…)
- Keijsers NL, Stolwijk NM, Nienhuis B, Duysens J., Normalization of plantar pressure pattern to use sophisticated analysis techniques – presentation (…)
- Kimmeskamp S, Hennig EM., Heel to toe motion characteristics in Parkinson patients during free walking. (…)
- Kirby K, Subtalar Joint Axis Location and Rotational Equilibrium Theory of Foot Function (…)
- Kopicera K; Piecha J, The fault analysis made by PSW data recorder for neurological disease classification (…)
- Lavery LA, Vela SA, Fleischli JG, Armstrong DG, Lavery DC., Reducing plantar pressure in the neuropathic foot. A comparison of footwear (…)
- Ledoux WR, Hillstrom HJ., The distributed plantar vertical force of neutrally aligned and pes planus feet (…)
- Lee S, Dynamic characterization of relative forefoot abduction (…)
- Lee WE, An Historical Appraisal and Discussion of the Root Model as a Clinical System of Approach in the Present Context of Theoretical Uncertainty (…)
- Leumann A, Pagenstert G, Fuhr P, Hintermann B, Valderrabano V., Intramedullary screw fixation in proximal fifth-metatarsal fractures in sports: clinical and biomechanical analysis. (…)
- Lewis GS, Kirby KA, Piazza SJ., Determination of subtalar joint axis location by restriction of talocrural joint motion. (…)
- Liddle D, Rome K, Howe T., Vertical ground reaction forces in patients with unilateral plantar heel pain – a pilot study. (…)
- Liikavainio T, Isolehto J, Helminen HJ, Perttunen J, Lepola V, Kiviranta I, Arokoski JP, Komi PV., Loading and gait symmetry during level and stair walking in asymptomatic subjects with knee osteoarthritis: importance of quadriceps femoris in reducing impact force during heel strike? (…)
- Liu XC, Thometz JG, Tassone C, Barker B, Lyon R., Dynamic plantar pressure measurement for the normal subject: Free-mapping model for the analysis of pediatric foot deformities. (…)
- Liu, X., Kim, W.D. and Drerup, B, Object Quantification of the foot arch a direct way by curvature (…)
- Long JT, Klein JP, Sirota NM, Wertsch JJ, Janisse D, Harris GF., Biomechanics of the double rocker sole shoe: gait kinematics and kinetics. (…)
- Lord M, Hosein R., A study of in-shoe plantar shear in patients with diabetic neuropathy. (…)
- Lorei TJ, Kinast C, Klärner H, Rosenbaum D., Pedographic, clinical, and functional outcome after scarf osteotomy. (…)
- Lott DJ, Hastings MK, Commean PK, Smith KE, Mueller MJ., Effect of footwear and orthotic devices on stress reduction and soft tissue strain of the neuropathic foot. (…)
- Macellari V, Giacomozzi C., Multistep pressure platform as a stand-alone system for gait assessment. (…)
- Mackey JR, Davis BL., Simultaneous shear and pressure sensor array for assessing pressure and shear at foot/ground interface. (…)
- Mackey JR, Davis BL., Simultaneous shear and pressure sensor array for assessing pressure and shear at foot/ground interface. (…)
- Mackey JR, Davis BL., Simultaneous shear and pressure sensor array for assessing pressure and shear at foot/ground interface. (…)
- Manor B, Wolenski P, Guevaro A, Li L., Differential effects of plantar desensitization on locomotion dynamics. (…)
- Mao de W, Li JX, Hong Y., Plantar pressure distribution during Tai Chi exercise. (…)
- Mao DW, Li JX, Hong Y., The duration and plantar pressure distribution during one-leg stance in Tai Chi exercise. (…)
- Martínez-Nova, Cuevas-García, Pascual-Huerta and Rodríguez, BioFoot® in-shoe system: Normal values and assessment of the reliability and repeatability (…)
- Menz HB , Alternative techniques for the clinical assessment of foot pronation (…)
- Menz HB, Morris ME., Clinical determinants of plantar forces and pressures during walking in older people. (…)
- Menz HB, Zammit GV, Munteanu SE., Plantar pressures are higher under callused regions of the foot in older people. (…)
- Mickle KJ, Steele JR, Munro BJ., The feet of overweight and obese young children: are they flat or fat? (…)
- Miller A, Sports podiatry a retrospective study to investigate if foot type is an indicator to the type of injuries that might occur in recreational walkers (…)
- Monteyne P, Studie van de functie van de voet bij de beweging van één- en tweepotige systemen (…)
- Mueller MJ, Zou D, Bohnert KL, Tuttle LJ, Sinacore DR., Plantar Stresses on the Neuropathic Foot During Barefoot Walking. (…)
- NAGEL A; FERNHOLZ F; KIBELE C; ROSENBAUM D, Long distance running increases plantar pressures beneath the metatarsal heads A barefoot walking investigation of 200 marathon runners (…)
- Nawata K, Nishihara S, Hayashi I, Teshima R., Plantar pressure distribution during gait in athletes with functional instability of the ankle joint: preliminary report. (…)
- Nicolopoulos C; Anderson E, Solomonidis S, Giannoudis P, Evaluation of the gait analysis FSCAN pressure system: clinical tool or toy? (…)
- Nicolopoulos C; Barnett S, Plantar Pressure Review using the FSCAN system (…)
- Nigg B, Hintzen S, Ferber R., Effect of an unstable shoe construction on lower extremity gait characteristics. (…)
- Nikolaidou M, Boudolos K, A footprint-based approach for the rational classification of foot types in young schoolchildren (…)
- Novak P, Burger H, Tomsic M, Marincek C, Vidmar G., Influence of foot orthoses on plantar pressures, foot pain and walking ability of rheumatoid arthritis patients-a randomised controlled study. (…)
- NYSKA M. ; LIBERSON A.; MCCABE C.; LINGE K.; KLENERMAN L., Plantar foot pressure distribution in patients with Hallux valgus treated by distal soft tissue procedure and proximal metatarsal osteotomy (…)
- Oh-yun K, Do-young J, Kyoung-hee P, The effect of rear foot wedge ankle on peak plantar pressures on forefoot during walking (chinese) (…)
- Orendurff MS, Rohr ES, Segal AD, Medley JW, Green JR 3rd, Kadel NJ., Regional foot pressure during running, cutting, jumping, and landing. (…)
- O’Sullivan K, Kennedy N, O’Neill E, Ni Mhainin U, The effect of low-dye taping on rearfoot motion and plantar pressure during the stance phase of gait. (…)
- Pataky TC, Caravaggi P, Savage R, Crompton RH., Regional peak plantar pressures are highly sensitive to region boundary definitions (…)
- Pataky TC, Caravaggi P, Savage R, Parker D, Goulermas JY, Sellers WI, Crompton RH., New insights into the plantar pressure correlates of walking speed using pedobarographic statistical parametric mapping (pSPM). (…)
- Pataky TC, Goulermas JY, Crompton RH, A comparison of seven methods of within-subjects rigid body pedobarographic image registration (…)
- Pataky TC, Goulermas JY., Pedobarographic statistical parametric mapping (pSPM): a pixel-level approach to foot pressure image analysis. (…)
- Paton J, Woodrow T, Passmore C, The Effect of Plantar Cover Padding with U’d Cut Out on Plantar Foot Pressure (…)
- Paton J; Stenhouse E; Jones R; Bruce G, Custom-made total contact insoles and prefabricated functional diabetic insoles: a case report (…)
- Payne C, Turner D, Miller K., Determinants of plantar pressures in the diabetic foot (…)
- Perry JE, Hall JO, Davis BL., Simultaneous measurement of plantar pressure and shear forces in diabetic individuals (…)
- Perttunen J, Foot loading in normal and pathological walking (…)
- Petre M, Investigating the Internal Stress/strain State of the Foot Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Finite Element Analysis (…)
- Praet SF, Louwerens JW., The influence of shoe design on plantar pressures in neuropathic feet. (…)
- Prasanna L, Ratnesh K, Tibarewala D, Gait Measures and Dynamic Weight bearing in Young and Elder Trans-tibal Amputee using PTB Prosthesis with SACH foot (…)
- Putti A, Arnold G, Cochrane L , Abboud R, Normal pressure values and repeatability of the Emed® ST4 system (…)
- Queen RM, Haynes BB, Hardaker WM, Garrett WE Jr., Forefoot loading during 3 athletic tasks. (…)
- R. P. Betts, C. I. Franks, T. Duckworth and J. Burke, Static and dynamic foot-pressure measurements in clinical orthopaedics (…)
- Rai D; Aggarwal L, Plantar pressure changes in normal and pathological foot during bipedal standing (…)
- Randolph AL, Nelson M, Akkapeddi S, Levin A, Alexandrescu R., Reliability of measurements of pressures applied on the foot during walking by a computerized insole sensor system. (…)
- Rao S, Saltzman C, Yack HJ., Ankle ROM and stiffness measured at rest and during gait in individuals with and without diabetic sensory neuropathy. (…)
- Raspovic A; Newcombe L; Lloyd J; Dalton E, Effect of customized insoles on vertical plantar pressures in sites of previous neuropathic ulceration in the diabetic foot (…)
- Renneboog B, Musch W, Vandemergel X, Manto MU, Decaux G., Mild chronic hyponatremia is associated with falls, unsteadiness, and attention deficits. (…)
- Rodgers MM, Cavanagh PR., Glossary of biomechanical terms, concepts, and units. (…)